GatlingX, spearheaded by Oxford alumni with expertise in machine learning and reinforcement learning, has introduced ‘GPU-EVM,’ touted as the most high-performing Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) available, as per internal benchmark assessments.
GPU-EVM stands out as an EVM scaling solution so efficient that state-of-the-art reinforcement learning (RL)-based AI agents can be trained atop it, asserts its development team. It harnesses parallel execution across various Ethereum applications, aiding in training AI agents to identify security vulnerabilities.
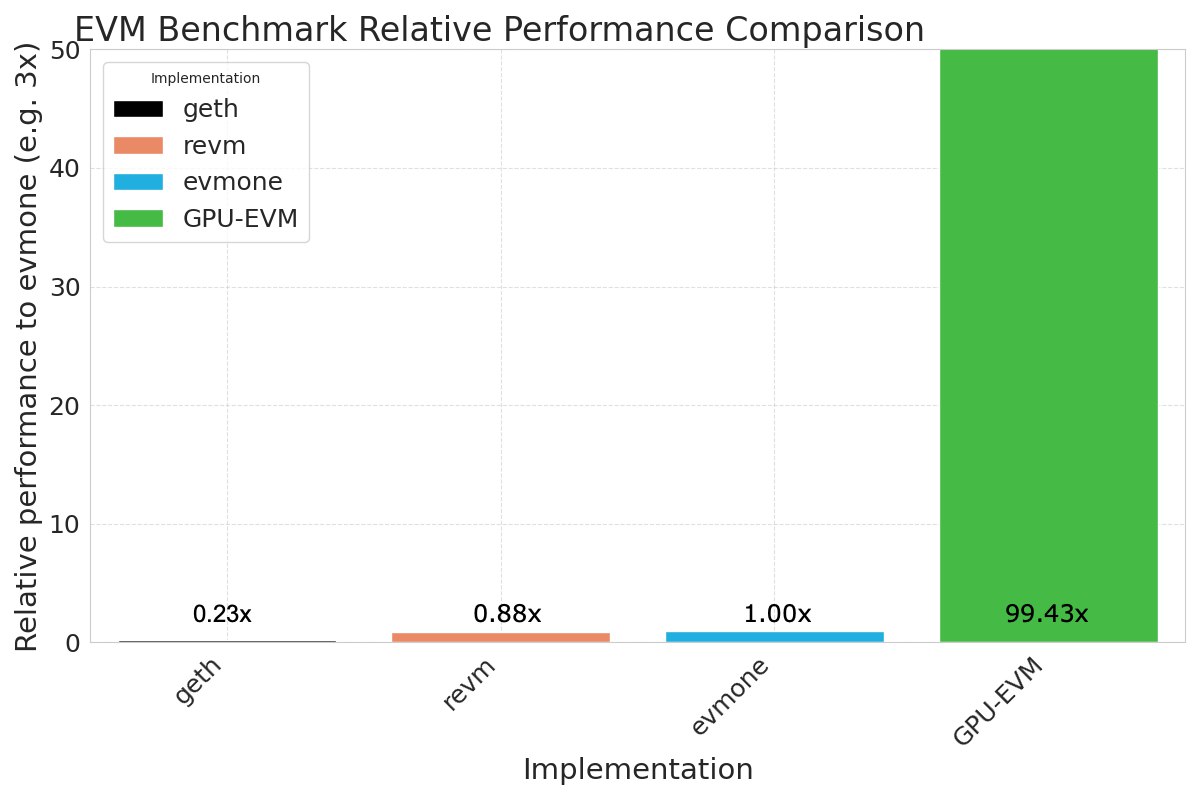
Employing graphical processing units (GPUs) for parallel execution, GPU-EVM enhances transactional throughput scalability significantly. The team asserts that GPU-EVM processes tasks nearly 100 times faster than current high-performance EVMs such as evmone and revm. This acceleration is chiefly attributed to GPUs’ capacity to handle multiple operations concurrently, leveraging their architecture inherently suited for parallel processing.
“Modern GPUs, equipped with thousands of cores, can concurrently handle multiple operations, making them exceptionally suited for parallel processing tasks. This inherent architectural advantage empowers GPU-EVM to execute a multitude of EVM instructions simultaneously, markedly boosting computation speeds and efficiency,” highlights the GatlingX team.
This development emerges amidst a burgeoning interest in parallel EVMs, driven by their potential to tackle blockchain scalability concerns. Traditional EVM implementations process transactions sequentially upon arrival, leading to prolonged processing times and increased costs during peak transaction volumes. In contrast, parallelized EVMs possess the capability to process multiple transactions concurrently, provided they are independent of one another.
The GPU-EVM is tailored to facilitate the training of AI agents within a parallel simulation environment, according to Eito Miyamura, co-founder, as conveyed to The Block. These agents undergo training to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in smart contracts, a process likened to the strategic gameplay involved in defeating Go world champions, reminiscent of the AlphaGo scenario of the mid-2010s.
Comparable to Nvidia’s Isaac Gym and Google’s Brax, this technology permits parallel simulations on GPUs for accelerated reinforcement learning training and boasts broad applications, Miyamura elaborated.
The initial phase of GPU-EVM’s rollout centers on establishing hardware-scaled EVM infrastructure, facilitating the training of AI and RL models. These models will interact with various components such as accelerated Layer 2 solutions, maximal extractable value (MEV) operations, and backtesting scenarios.
Subsequent phases, anticipated within a year, entail providing API access for high-performance computing applications, with the ultimate objective of surpassing human capabilities in securing smart contracts and decentralized applications.